AI Path Planning for Laser Cutting with Priority Constraints
Shanghai Jiao Tong University — Bachelor Thesis
Role: Undergraduate Researcher • Focus: Heuristic Algorithms & Deep Reinforcement Learning • Tools: Python, PyTorch
Introduction / Social Motivation
Laser cutting is widely used in modern manufacturing for metals, textiles, and other materials, and its economic value depends heavily on how efficiently the tool path is planned across hundreds of parts on a sheet. The path planning problem is NP-hard and further complicated by real production constraints such as contour nesting (inner holes must be cut before outer profiles) and priority rules imposed for quality and scheduling. Traditional heuristic algorithms like simulated annealing or genetic algorithms can provide good solutions, but they become slow or unstable when the number of contours exceeds 100, which is common in industrial drawings. This motivates the use of AI-based methods that can reuse learned structure to deliver near–optimal paths much faster, while still respecting engineering constraints such as nesting and priority ordering.
System Design & Methods
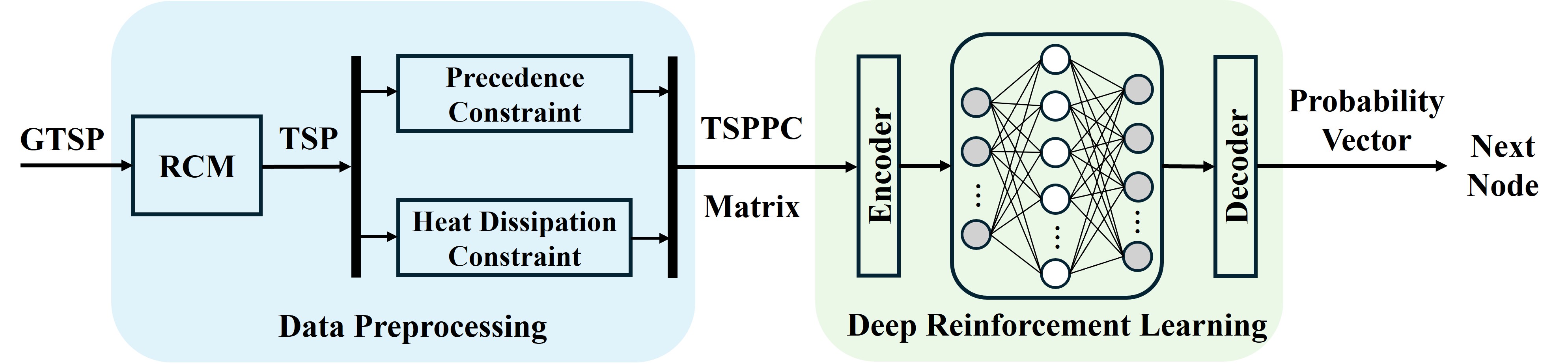
- Formulated laser cutting tool-path planning as a constrained optimization problem with nesting and priority constraints; discretized each contour into point sets and modeled the problem as a Generalized Traveling Salesman Problem (GTSP).
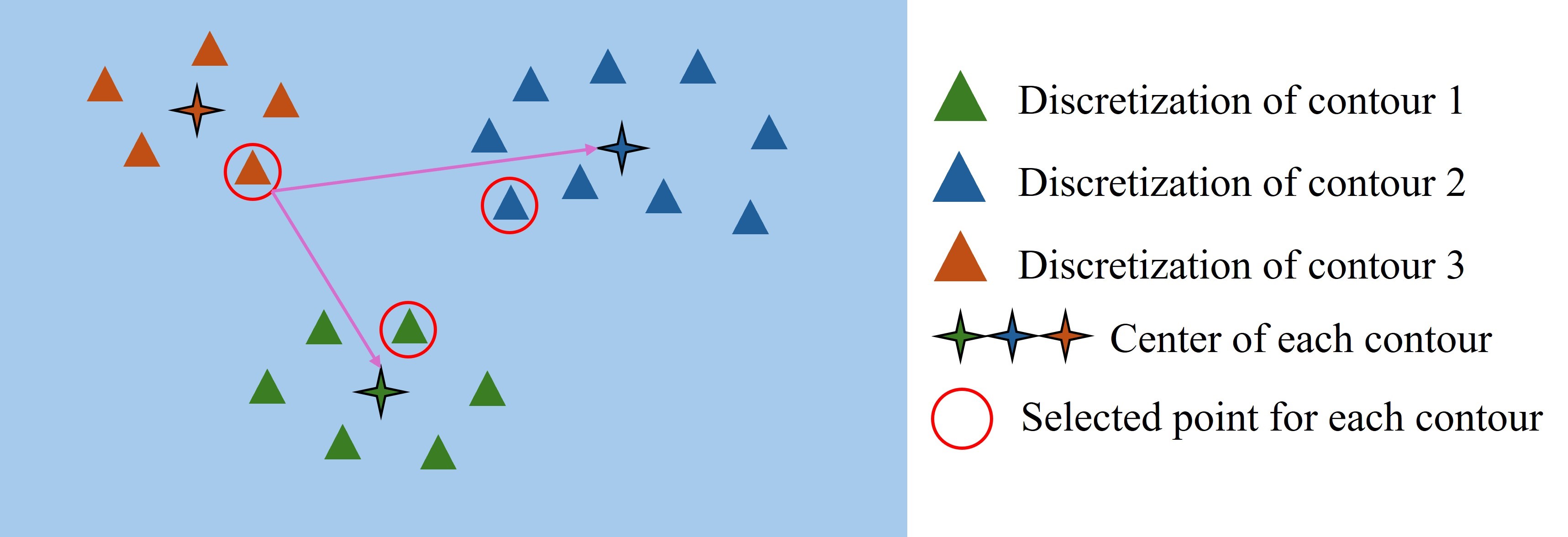
- Simplified GTSP instances into classical TSP by pre-selecting entry/exit points using geometric center–based strategies, and unified all instances into an adjacency-matrix format suitable for large-scale batch solving and learning.
- Implemented and compared several mature heuristic baselines (Simulated Annealing, Tabu Search, Ant Colony Optimization, Genetic Algorithms) to understand their runtime and solution-quality behavior on large GTSP/TSP instances.
- Designed a Deep Reinforcement Learning model with heterogeneous and sparse attention to construct TSP tours; trained it on a large corpus of randomly generated TSP instances from a custom problem generator.
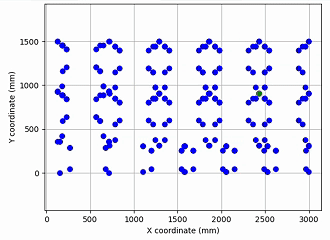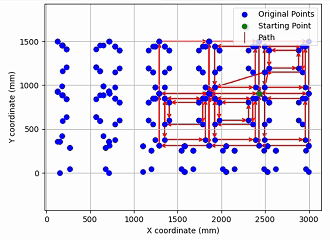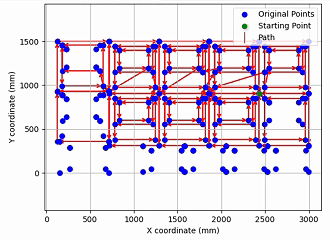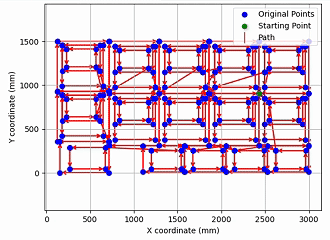
- Evaluated the trained DRL policy against state-of-the-art solvers such as LKH-3 and Nearest Neighbor, then mapped TSP solutions back to feasible cutting paths that satisfy nesting and priority constraints on real industrial laser-cutting drawings.
Results / Evaluation
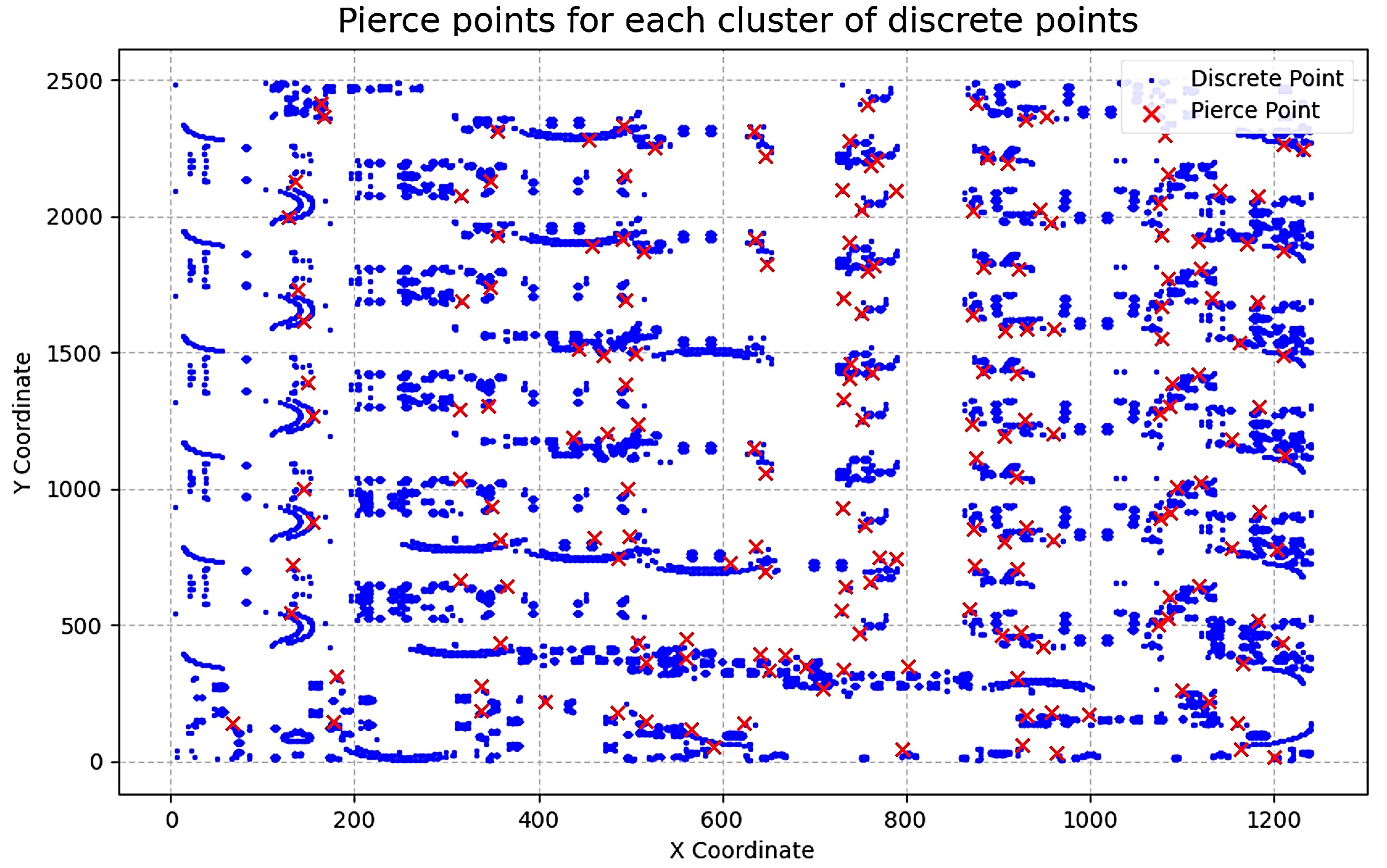
Experiments on large synthetic TSP benchmarks and real laser-cutting drawings show that the proposed DRL model can solve most instances two orders of magnitude faster than traditional heuristic methods, while keeping tour length within about 10% of LKH-3 for many cases with priority constraints. For GTSP problems exceeding 100 nodes, classical heuristics often require several minutes of runtime or even cause kernel crashes, whereas the trained policy maintains stable inference time on the same scale of problems. The GTSP–to–TSP conversion pipeline was validated to be unbiased using enumeration and simulated annealing on smaller instances, confirming that solutions in the transformed space can be reliably mapped back to valid cutting paths. Some specific contour distributions still lead to degraded solution quality, highlighting directions for future model refinement and constraint-aware training.
My Contribution
- Built the complete mathematical formulation of the laser cutting path planning problem, including nesting and priority constraints, and implemented the GTSP and TSP representations.
- Developed the preprocessing pipeline that discretizes contours, selects entry/exit points, and converts industrial drawings into adjacency-matrix TSP instances.
- Implemented and tuned multiple heuristic baselines, then designed experiments to compare their runtime and solution quality on large-scale GTSP/TSP problems.
- Implemented the heterogeneous-attention DRL model and custom TSP instance generator in Python/PyTorch, conducted large-scale training, and integrated the model into the end-to-end solving pipeline.
- Applied the trained solver to real laser-cutting drawings provided by industry partners, analyzed failure cases for difficult contour patterns, and wrote the full bachelor thesis documenting the methodology and results.
Artifacts
- Python/PyTorch implementation of the heterogeneous-attention DRL solver for TSP-based path planning.
- Preprocessing tools that convert laser-cutting CAD drawings with nesting and priority constraints into GTSP/TSP instances.
- Benchmark scripts comparing DRL against classical heuristics (SA, Tabu, ACO, GA, LKH-3, NN) on large-scale problems.
- Visualization notebooks for plotting cutting paths, contour nesting relationships, and solution-quality statistics.
- Full bachelor thesis report “Research on AI Algorithms for Path Planning of Laser Cutting with Priority Constraints.”
- Presentation slides summarizing problem formulation, DRL architecture, and experimental results.